Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment of Vitiligo and Guidelines for Home Phototherapy
Overview of Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a common skin depigmentation disease with a prevalence of about 0.5%. It is a localized acquired depigmentation spot of the skin caused by the reduction or loss of functional melanocytes in the skin and (or) hair follicles.
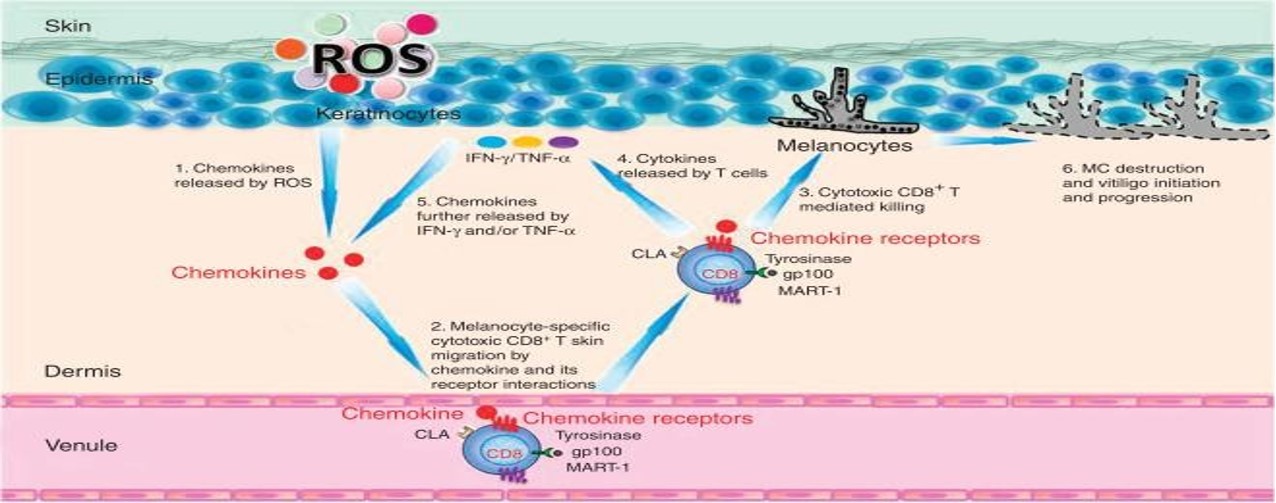
Pathogenesis of Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a common primary, localized or generalized skin depigmentation disorder caused by a reduction or loss of functional melanocytes in the skin or hair follicles. So far, its etiology and pathogenesis have not been elucidated, and the pathogenesis hypotheses mainly include genetics, immunity, oxidative stress, and ultraviolet damage mechanisms.
Genetic theory The onset of vitiligo is related to heredity, and there is a certain phenomenon of family aggregation, showing polygenic inheritance, and 10% to 38% of patients have a family history. So far, about 120 genes have been found to be related to the onset of vitiligo. | Immunology Vitiligo patients are likely to be accompanied by the onset of autoimmune diseases, such as autoimmune thyroiditis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc. Various cells and autoantibodies participate in the damage or death of melanocytes, leading to the occurrence of diseases. |
| Oxidative stress theory Excessive oxidative stress products have a direct toxic effect on melanocytes, affect melanin metabolism to a large extent, and can lead to the survival of melanocytes in severe cases. | Mechanisms of UV damage Numerous studies have found that the onset of vitiligo is related to the seasons, and the onset is most serious in summer, followed by spring. The main site of attack is the head and neck, which may be related to the fact that this part receives the most ultraviolet radiation. |
Stages of Vitiligo: Progressive and Stable
VIDA score: New skin lesions or enlargement of existing skin lesions in the past 6 weeks (+4)
New skin lesions or enlargement of existing skin lesions in the past 3 months (+3)
New skin lesions or enlargement of existing skin lesions in the past 6 months (+2)
New skin lesions or enlargement of existing skin lesions in the past 1 year (+1)
Stable for at least 1 year (0)
Stable for at least 1 year with spontaneous pigment regeneration (-1)
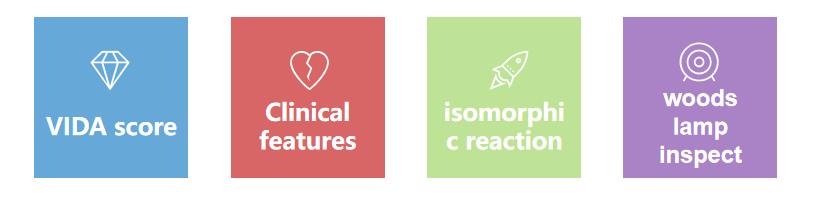
Stable Period vitiligo Judgment:
① VIDA points are 0 points;
②Clinical features: The leukoplakia is porcelain white with clear edges or pigmentation;
③No isomorphic reaction (≥ 1 year);
④Wood's lamp: The skin lesions are white in color with clear borders, and the area of skin lesions under Wood's lamp ≤ visual area.
If the above conditions are met, it is indicated as a stable period, and if the above conditions are not met, it is indicated as an Progressive period vitiligo.
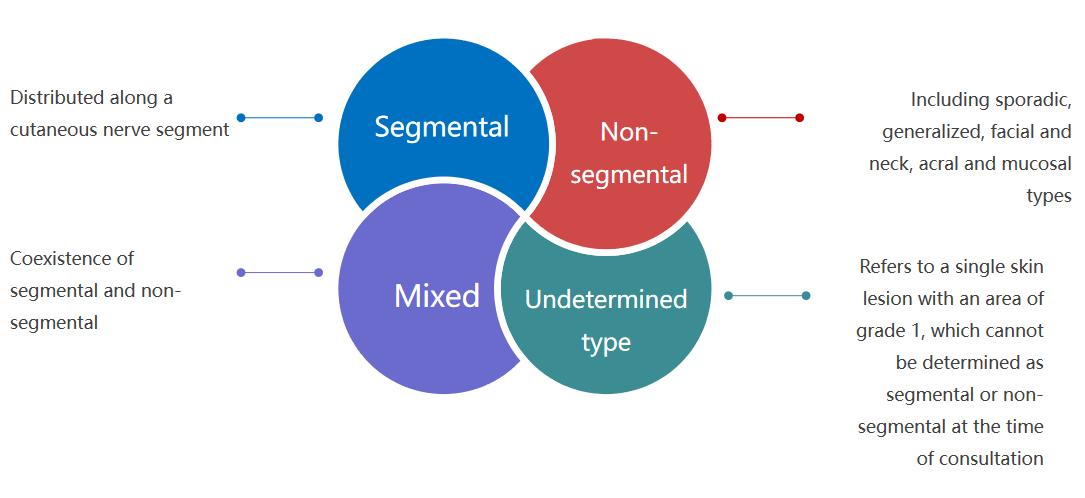
Types of Vitiligo
Distinguishing Vitiligo from Other Skin Disorders
we can distinguish vitiligo from other skin conditions by a woods lamp
|  |
Common treatment methods for vitiligo
Phototherapy: Local phototherapy (NB-UVB, 308nm ultraviolet light) and systemic NB-UVB phototherapy are suitable for patients in advanced and stable stages. Select different initial treatment doses according to different parts, or measure the minimum erythema dose (MED) before treatment, the initial dose is 70% MED, 2-3 times a week. The dose of phototherapy in the stage of rapid progression should be 1/2 - 1/3 of the normal initial dose, which can start from 100mJ/cm2. It can be used in combination with systemic hormones or antioxidants to avoid oxidative stress caused by phototherapy and the expansion of skin lesions.
Hormone therapy: Topical and systemic corticosteroids are generally used in the advanced stage, and early use of hormones can stabilize the advanced stage of vitiligo. Topical corticosteroids should be avoided around the eyes; for patients with contraindications to systemic corticosteroids, other immunosuppressants may be considered as appropriate.
Calcineurin inhibitors: Topical calcineurin inhibitors include tacrolimus ointment and pimecrolimus cream. The treatment time is 3-6 months, and the intermittent application can be longer. Recolor works best on the face and neck. Special parts such as the periorbital area should be used first, and the oral mucosa and genital area can also be used. These drugs have no adverse reactions caused by hormones, but they can still cause or aggravate local infections such as folliculitis, acne, and herpes simplex.
Vitamin D3 derivatives: calcipotriol ointment and tacalcitol ointment for external use can be used to treat vitiligo, applied externally twice a day. Vitamin D3 derivatives can be combined with NB-UVB, 308nm excimer laser, etc. for treatment. It can also be combined with topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. Topical application of calcipotriol ointment or tacalcitol ointment can enhance the efficacy of NB-UVB in the treatment of vitiligo.
Depigmentation treatment: mainly applicable to patients with leukoplakia involving > 95% body surface area. Resistance to various methods of repigmentation treatment has been demonstrated, and skin depigmentation is acceptable at patient request. Strict sun protection is required after decolorization to avoid sun damage and recoloration. Includes depigmentation treatments and laser treatments.
What is UV Phototherapy?
In 1901, Dr. Finsen first proposed the use of ultraviolet light to treat skin tuberculosis infection, for which he won the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1903. Since then, various indications for phototherapy have been gradually discovered. |
Niels Ryberg Finsen(1860-1904) |
Ultraviolet therapy refers to the application of artificial light sources of ultraviolet light to treat skin diseases. It is a common treatment method in dermatology.
At present, the light source used in UVB and UVA ultraviolet treatment is mainly ultraviolet fluorescent lamps;
308nm excimer phototherapy uses "excimer" light-emitting technology, and uses xenon chloride gas as the medium to emit pure excimer light with a peak wavelength of 308nm.
Treatment Response to Home Light Therapy Device
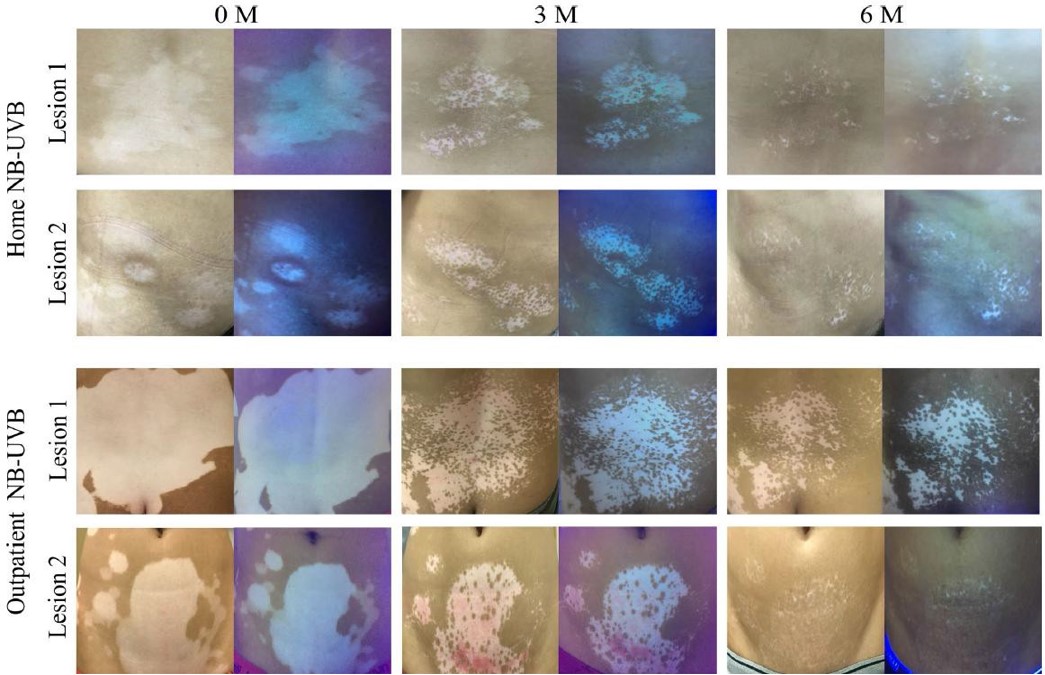
Zhang L, Wang X, Chen S, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety profile for home NB-UVB vs. outpatient NB-UVB in the treatment of non-segmental vitiligo: A prospective cohort study.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2019;35:261–267
Selection Tips of Home Phototherapy Device
(1) Choose a phototherapy instrument that is approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), has the "Registration Certificate for Medical Devices of the People's Republic of China" and clearly indicates that the object of use in the registration certificate can be used by patients themselves.
Products without NMPA certification lack the guarantee of safety and effectiveness. If the medical device is not clearly marked as "can be used by patients themselves", it is generally used in hospitals and needs to be operated and used by professional medical staff. Therefore, for home phototherapy, patients need to purchase phototherapy equipment that can be used by non-medical professionals with the words "for the patient's own use".
(2) Select according to the size and location of the patient's skin lesions
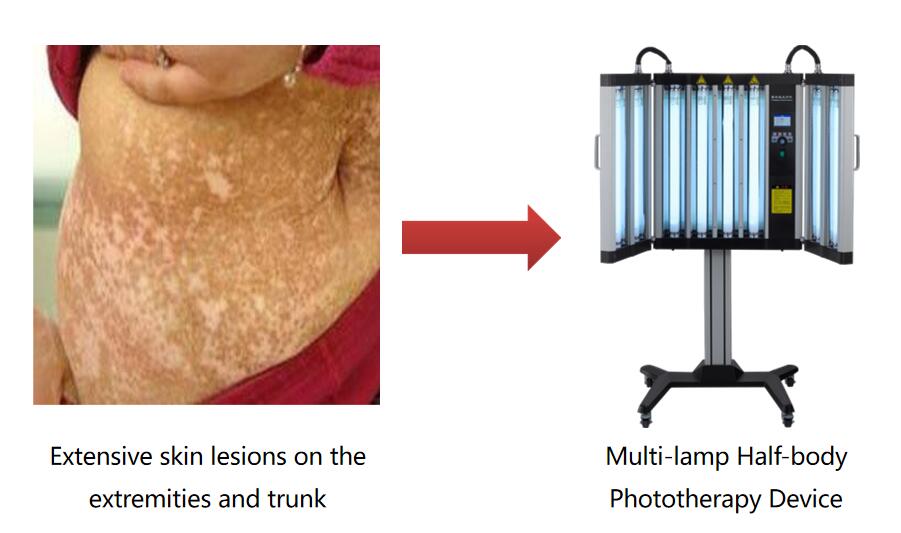
For large skin lesions or generalized skin lesions, it is recommended to use half-cabin phototherapy equipment
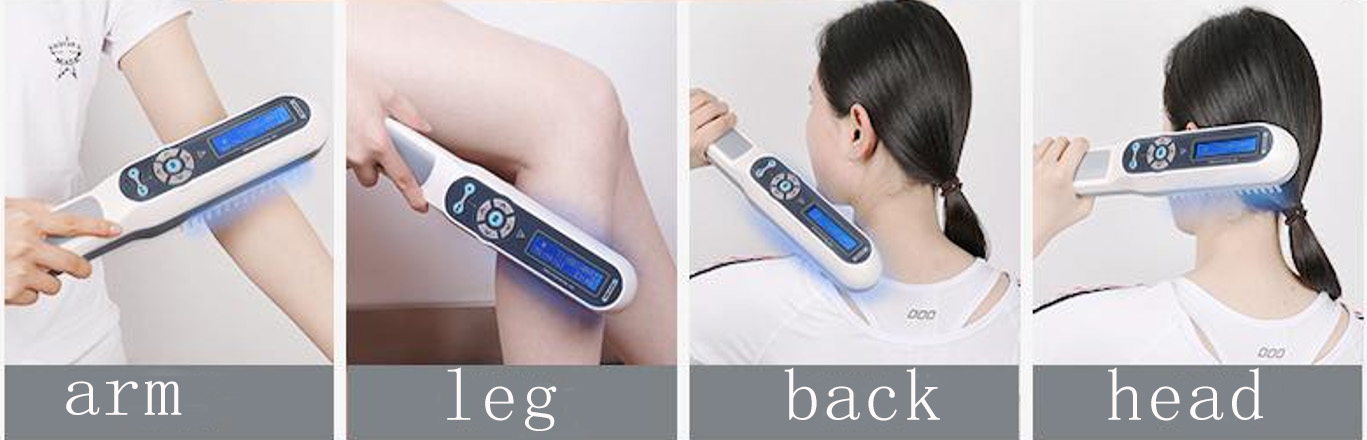
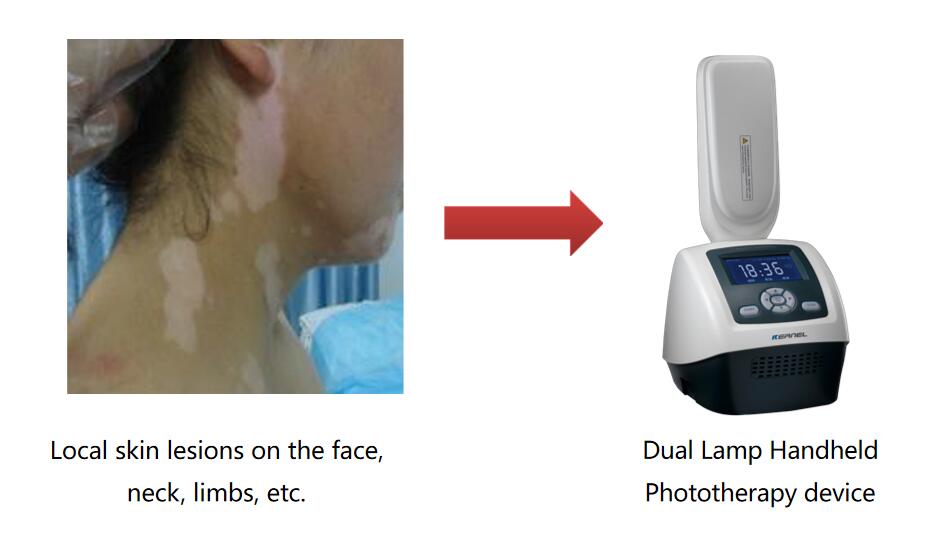
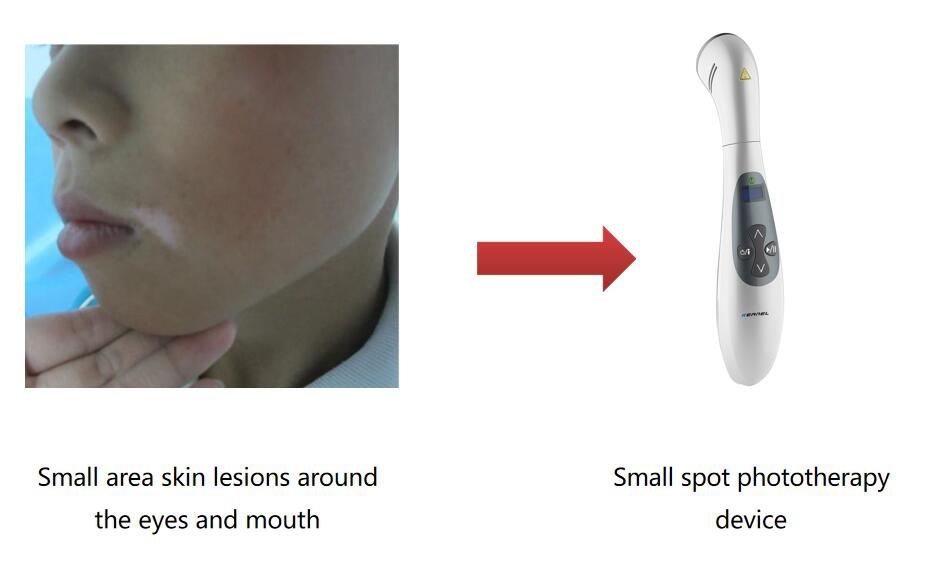
Handheld phototherapy device for patients with small lesions
For specific parts, such as skin lesions in the groin and underarms, a small-spot phototherapy device can be used
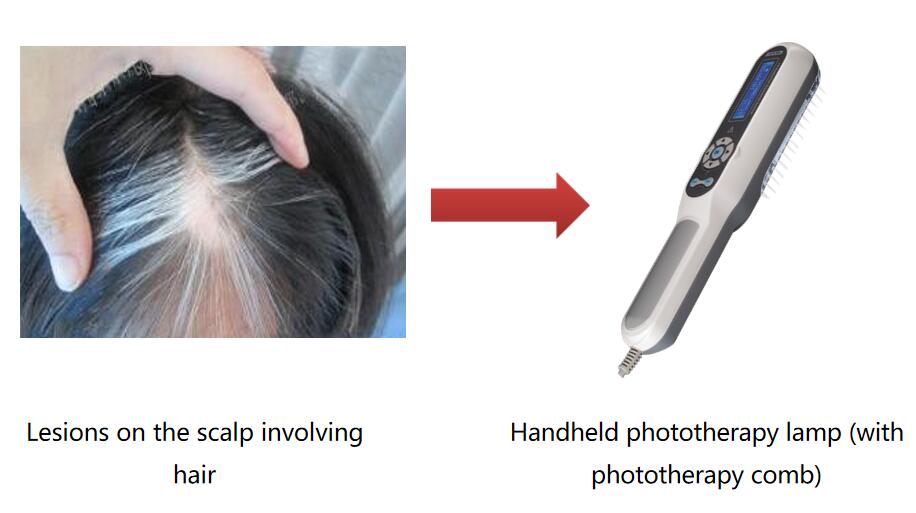
Scalp psoriasis/vitiligo, optional with specially designed phototherapy comb
(3) Choose a home phototherapy device that can directly set the dose mode or time mode to avoid insufficient or excessive exposure
Accurately grasping the time of each light exposure is conducive to better recovery of skin lesions, if the time is too short, the onset of effect will be slow, and if the time is too long, adverse reactions such as erythema and blisters will easily occur
Therefore, it is recommended that patients choose a home phototherapy device that can directly set the dose mode or time mode to help accurately reach the scheduled time of the treatment plan.
Precautions for using phototherapy in patients with vitiligo
?Patients should avoid taking photosensitivity food and medicine before receiving UV treatment
?Do not apply salicylic acid or thicker colored moisturizing cream within 4 hours before treatment to avoid blocking ultraviolet radiation and affecting the treatment effect
?During whole-body ultraviolet treatment, the unaffected face, neck, nipples and other parts can be covered with sunscreen or clothing, and special parts such as eyes and genitals can be covered with ultraviolet protective equipment
? When partial exposure to ultraviolet rays, you should also pay attention to protect your eyes to avoid corneal damage
?On the day after the ultraviolet treatment, the treatment area should avoid additional sunlight exposure, and if necessary, sunscreen or clothing can be applied to cover it, and the patient should avoid hot water baths