UVA1 phototherapy treatment morphea UV phototherapy
1. New technology high-power UV solid-state cold light source
2. Array type reflective light path design
3. Superconducting material to make the heat-conducting substrate
4. Irradiation intensity multi-grade adjustment function
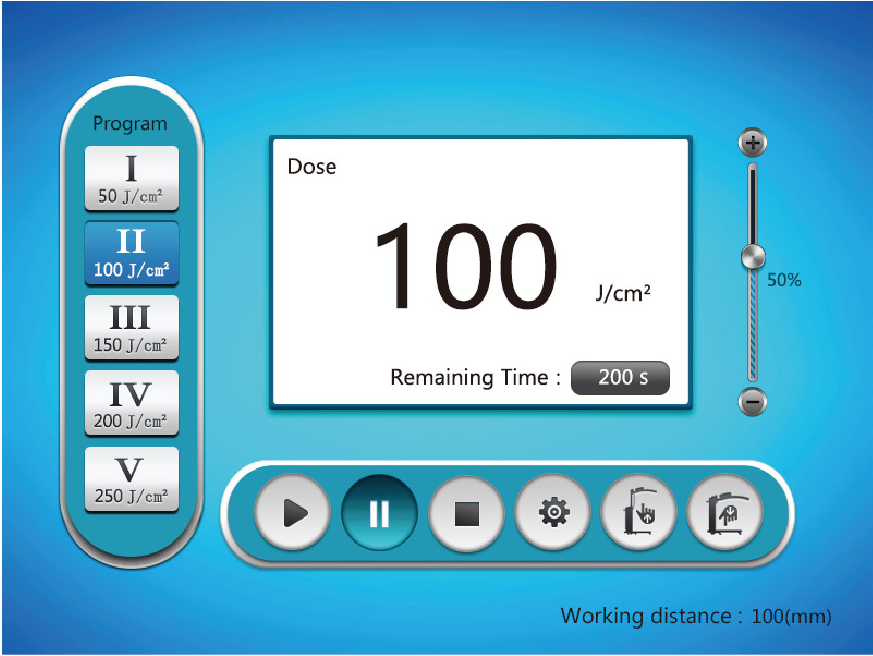
5. Five built-in conventional treatment programs
6. Built-in precision sensor for real-time monitoring
- Scleroderma
- ISO13485, CFDA
- UVA1
- available
Overview
| Solid-state Cold Light Source New technology high-power UV solid-state cold light source, high output energy, long service life. |
Superconducting Substrate Superconducting material to make the heat-conducting substrate, with the heat dissipation system based on the aerodynamic principle to ensure the reliable and stable work of the light source. |
|
| 8" Touch Screen 8'' capacitive touch screen with a large color character display for clear and easy-to-understand operating instructions. |
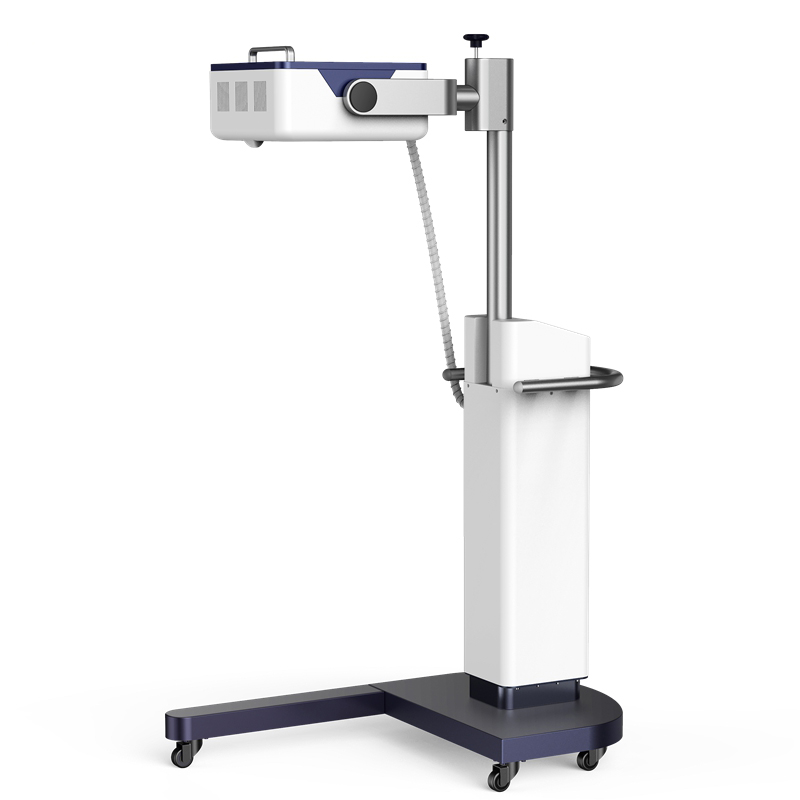
Flexible The ergonomic lifting mechanism of is very flexible for the operation of the treatment head and can meet the clinical needs. |
|
Features
1. New technology high-power UV solid-state cold light source, high output energy, long service life.
2. Array type reflective light path design, the light source output is more uniform.
3. Superconducting material to make the heat-conducting substrate, with the heat dissipation system based on the aerodynamic principle to ensure the reliable and stable work of the light source.
4. The large treatment area of can meet more diversified clinical treatment needs.
5. Irradiation intensity multi-grade adjustment function, fully meet the individualized treatment of patients with different degrees of tolerance.
6. The ergonomic lifting mechanism of is very flexible for the operation of the treatment head and can meet the clinical needs.
7. The solid base and trolley of ensure the safety of the device's operation while enhancing its mobility and flexibility.
8. 8'' capacitive touch screen with a large color character display for clear and easy-to-understand operating instructions.
9. Five built-in conventional treatment programs to make the operation more convenient.
10. Irradiation intensity calibration function, used in conjunction with the dose mode, makes clinical treatment more accurate. (4002A1 is applicable)
11. Built-in precision sensor for real-time monitoring of light source usage, making equipment operation more stable and reliable.
Specification
Irradiation Area | 4002A1: 1600cm2±10% |
| 4002A2: 1024cm2±10% | |
| Working Distance | 5cm±1cm |
| Size | 650mm×1139.5mm×1124mm |
| Working Voltage | AC 220V, 50Hz |
| Irradiation Intensity | 4~50 mW/cm2 |
| Irradiation Dose | ≤200J/cm2 |