Clinical application of ultraviolet light therapy in the treatment of psoriasis
Clinical application of ultraviolet light therapy in the treatment of psoriasis
Kernel Medical specially invited Professor Li Fuqiu from the Second Hospital of Jilin University to tell us about the clinical application of ultraviolet light therapy in the treatment of psoriasis.
The content of this course is aimed at eliminating skin lesions, hypopigmentation, and reducing pruritus in psoriasis, focusing on the principles of psoriasis treatment, the important position of ultraviolet light therapy in the treatment of psoriasis, the treatment plan and precautions of ultraviolet light therapy, etc. Expansion of the content.
1
Overview and clinical manifestations of psoriasis
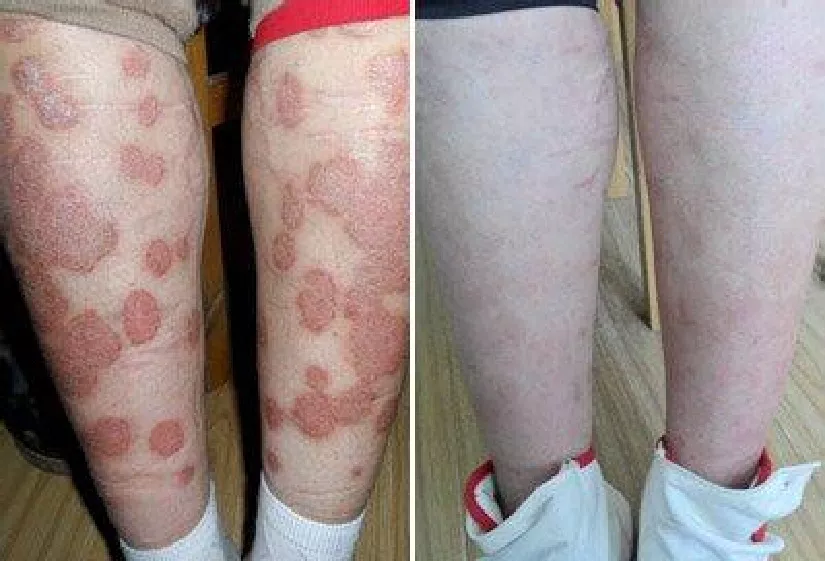
Psoriasis is a chronic, recurrent, inflammatory, and systemic disease induced by the interaction of genetics and environment and immune-mediated.
The typical clinical manifestations are scaly erythema and plaques, which are localized or widely distributed, non-infectious, difficult to treat, and often suffer for life.

2
Conventional treatment for psoriasis
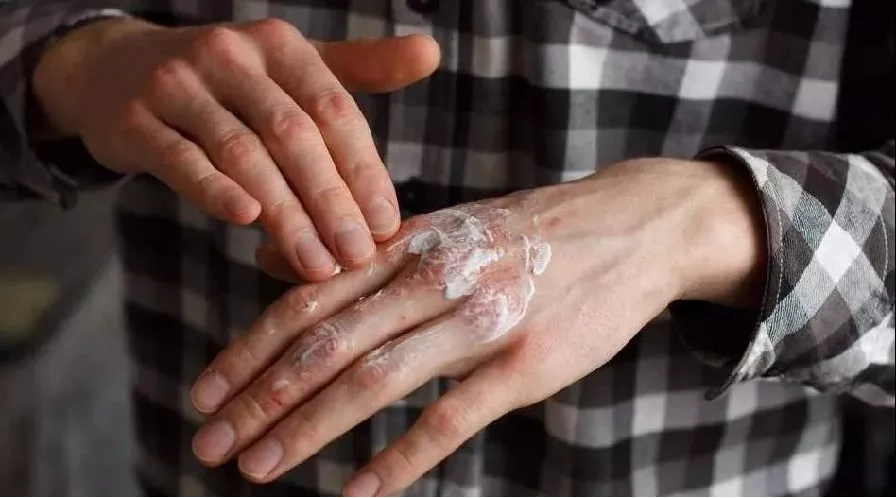
Topical drugs are the first-line treatment for mild to moderate psoriasis. The choice of topical drugs and their treatment options is based on the patient’s age, medical history, type and course of psoriasis, and skin lesions. Commonly used drugs are glucocorticoids, vitamin D3 derivatives, tretinoin and so on. Patients with scalp psoriasis with moderate to severe skin lesions are recommended to systematically use conventional oral drugs or biological agents such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and tretinoin.
3
Difficulties in treatment
Psoriasis itself tends to recur and is more stubborn, making it more difficult to treat than other skin diseases. Because of the presence of skin lesions, scales or hair, it is difficult to administer topical drugs and the patient's compliance is poor. Oral drugs have a single effect and often need to be used in conjunction with other treatments.
Featured Questions Answers
Q: What are the most common ultraviolet light therapy?
There are two types of light therapy for psoriasis:
(1) Photochemotherapy (PUVA);
(2) Narrow-band mid-wave ultraviolet (NB-UVB);
Narrow-band UVB (311nmUVB) phototherapy is currently recognized as one of the first choices for the treatment of psoriasis.
Q: Do I need to do a photosensitivity test before phototherapy?
Before the initial phototherapy, the MED (minimum erythema) test can be used to determine the initial exposure dose/time suitable for your skin, or you can directly use the recommended initial exposure dose/time for irradiation.
Q: What should I do if skin itching occurs after exposure to light?
After receiving local light, most patients will have symptoms of skin itching to varying degrees, usually because the skin is in a state of dehydration. You can apply moisturizing lotion after exposure to keep the skin hydrated and help relieve itching.
Q: Will long-term exposure cause skin cancer?
So far, many investigations have been conducted on the correlation between phototherapy, photochemotherapy and skin cancer, and all the results have failed to confirm that phototherapy and photochemotherapy can directly cause skin cancer.
Q: Are there any side effects of phototherapy? What to do if it happens?
Compared with drugs, ultraviolet light therapy has mild side effects. The most common ones are local erythema, pain and other sunburn-like reactions caused by excessive radiation dose or excessive radiation frequency. If it occurs, you can suspend the irradiation first, and continue the treatment after the erythema subsides. If there are severe erythema or blisters, you can go to the hospital to see a doctor for a face-to-face treatment, and then continue treatment after local treatment and improvement.
